Place
Category: Marketing
Products can reach customers in several ways. Customers can either obtain them directly from the factory or through a variety of distribution channels. The structure of the distribution channels plays a major role in the marketing mix.
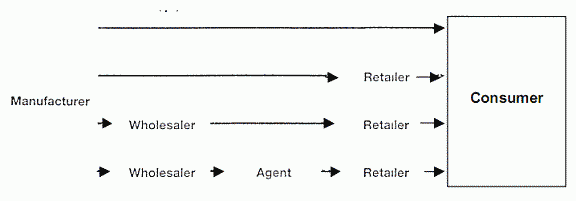
Distribution channel for consumers goods
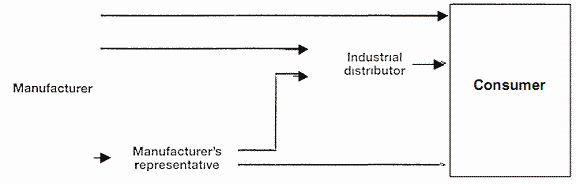
Distribution channel for industrial goods
The choice of a distribution channel is a long term decision that cannot easily be changed. Also, the manufactures influence on prices can be sight after the product enters the distribution channel.
In some situations a distribution channel must consider the middleman as the most convenient market place for the manufacturer. His prestige on the consumer market may well be greater than the manufacturer ‘s. Nevertheless, the distribution channels are in most cases absolutely necessary for the manufacturer. For example, it is difficult to imagine a company selling chewing gum in special stores or through travelling salesmen. Most producers would not even want to operate the distribution channel since their profit margin in the core business is higher than that of their retailers.
A distribution channel helps to link the producer with the customer and facilitates the necessary business transfers between them. A list of key functions of distribution channels is given below:
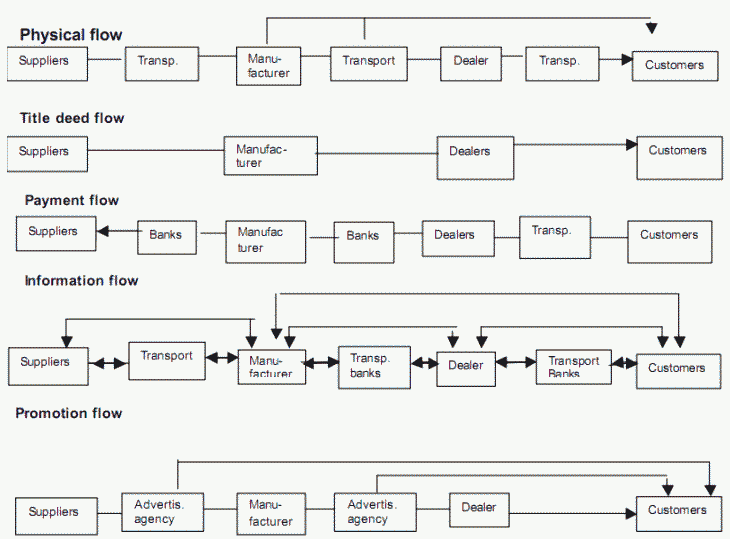
Information: the collection and dissemination for information about potential or current customers, competitors, and other actors and forces in the marketing environment.
Promotion: the development and dissemination of persuasive communication concerning the offer, designed to attract customers.
Negotiation: the attempt to reach final agreement on price and other terms so that transfer of ownership or possession can be effected.
Ordering: the backward communication of intentions to buy to the marketing channel members to the manufacturer.
Financing: the acquisition and allocation of funds required to finance inventories at different levels of the marketing channel.
Risk Taking: the assumption of risks connected with carrying out the channel work.
Physical Possession: the successive storage and movement of physical products from raw materials to the final customer.
Payment: buyers paying their bills through banks and other financial institutions to the sellers.
Title deed: the actual transfer of ownership from one organisation or person to another.
The marketing flows can be very complex since a single transaction normally initiates several flows of different nature.
Different marketing flows
Economic, control an adaptive criteria should be considered when a company selects a distribution channel for its products.
Criteria for the selection of a distribution channel
| Economic criteria | Each channel alternative will produce a different level of sales and costs |
| Control criteria | There must be means of motivating and evaluating the performance of the channel against criteria such as customer delivery time, cooperation in promotion, etc. |
| Adaptive criteria | Each channel involves some duration of commitment and loss of flexibility; during this period other distribution channels may become more effective. |
To evaluate the prospective intermediary closely one should take the following factors into account. In the process, one has to bear in mind that the choice of distribution channel is a long-term decision than can not be easily changed.
Budget and controls
Implementation of the marketing strategy must be carefully monitored so than one can react to unforeseen developments.
The people responsible for the various actions must report on the success of the actions. If the actions defined turn out not to be efficient, alternatives must be worked out in order to reach the objectives.
Examples of control ratios:
— Average number of sales contacts per sales person per day
— Average preparation time per contact
— Average revenue per sales contact
— Average cost per sales contact
— Entertainment cost per sales contact
— Percentage of orders per hundred sales contacts
— Number of new customers lost per period
— Salesforce cost as a percentage of total sales
Monitoring can be the responsibility of a steering committee, which should meet at monthly intervals.